Do you ever wait for a long period when setup an additional domain controller especially in branch environment and wait for it to replicate AD database? You may need to wait a bit longer especially when you have limited Internet connectivity.
Well, we do and we even tested to deploy a virtualized domain controller in branch and it only has 128K bandwidth. The connection was crawling like turtle speed and it took very long to replicate entire active directory database.
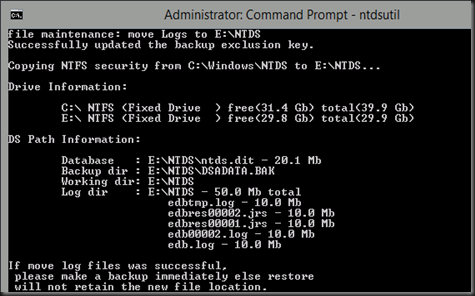
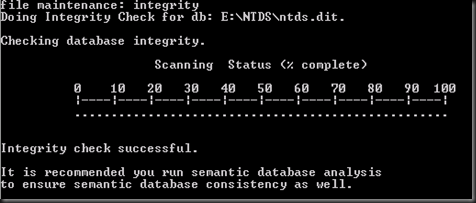
To solve this problem, we decided to use IFM (Install from media). To start with, make sure your existing domain controller
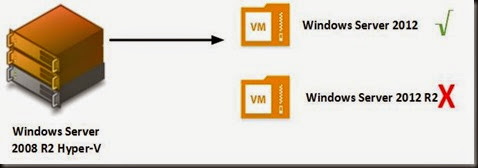
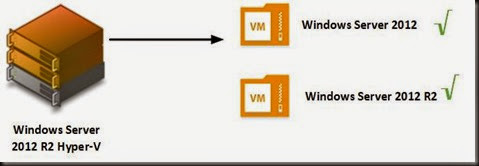
- running at least Windows Server 2012
- DNS
- Global catalog
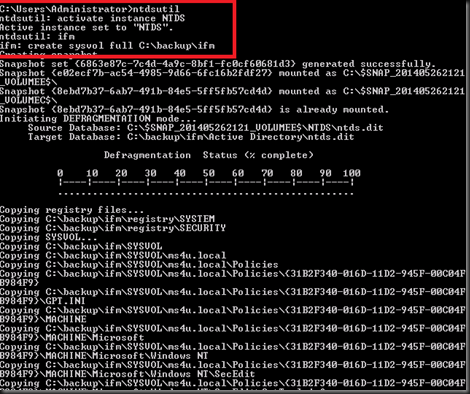
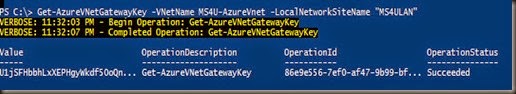
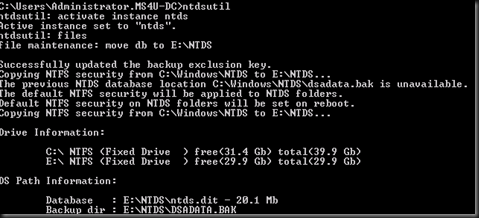
Use command prompt and type
|
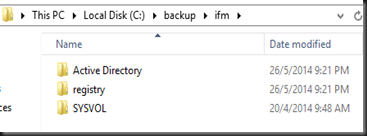
This process will store active directory database, registry and sysvol into C:\Backup\IFM
Once complete, transfer the entire folder in C:\backup to your branch virtualized domain controller. Now you have successful created an IFM using ntdsutil.
Next step is setup an additional domain controller at branch.
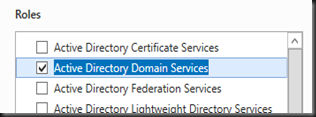
Make sure you have install Active Directory Domain Services roles and then configure DC using Server Manager.
Click “Promote this server to a domain controller”
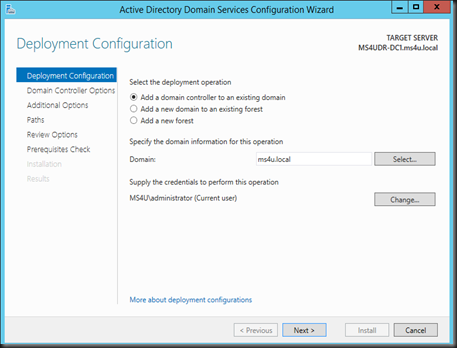
Select “Add a domain controller to an existing domain”
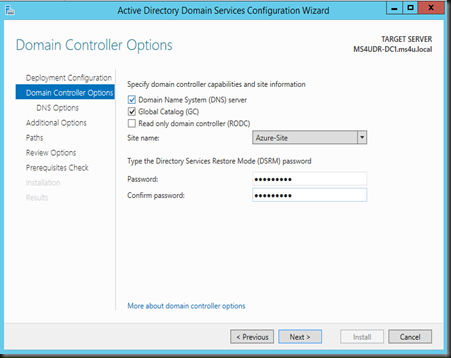
Select the site that you’ve created and enter Directory Service Restore Mode password”
IMPORTANT
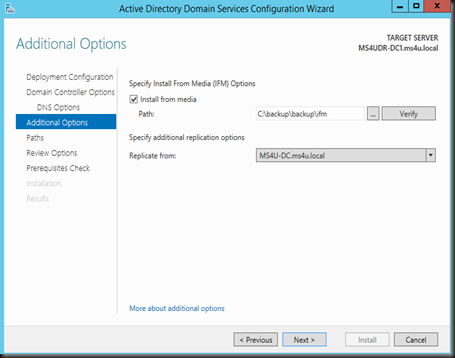
Select Install from media , define the path which consist your backup ntds and select replicate from nearest DC
Then Define the path of new active directory database to another path (normally another disk). For more info, you can check out “Best Practice on Virtualizing Domain Controller post”
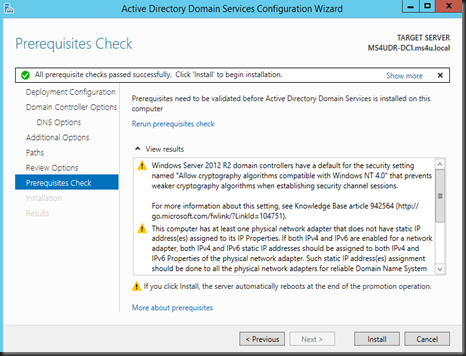
Click Install to start the installation
Verification
Verify that you can access the following snap-in:-
- Active Directory User and Computer
- Active Directory Sites and Services
- Active Directory Domain and Trust
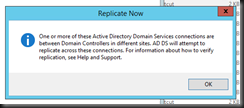
Lastly initiate force replication to sync with primary domain controller to get the latest active directory database.
Well, that’s all for now.
As a conclusion, by using IFM it can you a lot of time and also your network bandwidth. Give it a try if you do have multi site branch Active directory deployment.